Live resin is a relatively new type of cannabis concentrate or extraction. It has become popular among customers and producers alike—it retains the tastes and scents of the living plant better than other cannabis extracts and is less expensive and easier to produce.

The effect of a high-quality resin is consistent and powerful, making them ideal for outdoor uses. High-quality resins are often more complex in terms of terpene profile and can provide a more nuanced experience.
What is live resin?
Cannabis concentrates can be categorised by their texture or consistency, such as shatter, waxy, thick and gooey, and batter. Live resin is a more flexible concentrate that sits in between wax and sauce in terms of malleability—not quite like taffy yet not too wet either.
The buds are generally dark yellow in color, although they can range from light yellow to white. It’s sticky like all cannabis concentrates, so you’ll need a dab tool to work with it.
Red wood, earthy musk, and leaves are all found in cannabis resins. The high occurs almost immediately after consumption. It’s one of the most potent varieties available on the market today because it has a lot of THC. Consumers enjoy it since to its powerful tastes and aromas that linger from the original plant.
How to make live resin
 Fresh frozen cannabis—plants that are frozen immediately after being cut down at harvest—is used to create Resin. Fresh frozen cannabis distinguishes Resin from other types of cannabis concentrates because it is made from fresh frozen plants — plants that are immediately frozen after they have been harvested. During the extraction process, these plants are kept frozen and do not go through the drying, curing, or trimming phases of harvesting.
Fresh frozen cannabis—plants that are frozen immediately after being cut down at harvest—is used to create Resin. Fresh frozen cannabis distinguishes Resin from other types of cannabis concentrates because it is made from fresh frozen plants — plants that are immediately frozen after they have been harvested. During the extraction process, these plants are kept frozen and do not go through the drying, curing, or trimming phases of harvesting.
Cannabis plants’ drying and curing procedures might harm terpenes, the plant’s flavor and fragrance chemicals. Terpenes are present in trichomes, which cover buds as well as surrounding greenery.
When the plant has been exposed to sufficient moisture and light, it dries and cures. Moisture and chlorophyll are leaved as the plant dries and cures. Trichomes can be damaged by heat, air, and light while they are on the plant during harvesting. Trichomes also break off a crop when harvested manually or transported across each other during storage.
The plant’s valuable terpene profile, original flavor, and fragrance are preserved throughout the extraction process and into the final product by freezing it right after harvest. Trichomes are frozen in live resin, preserving them in their natural form.
Frozen plants are subjected to a solvent extraction procedure with butane, propane, or another solvent after harvest.
After harvest, here are the steps for creating live resin:
- Freeze plants/plant matter
- Extract the oil
- Process into live resin
During the extraction procedure, plants are kept at temperatures that stay below 0°F. After extracting, live resin is frequently heated in a vacuum oven. It can be preserved as-is or added to vape pen carts
Cured resin vs. live resin
The key distinction between these two concentrates is the starting source: Cured resin is produced from dried plant material, whereas live resin is created from frozen plant material that is maintained frozen throughout the extraction procedure.
Curing resin refers to cannabis extracts that will be transformed into shatter, wax, batter, or other types of concentrates after extraction from dry cannabis.
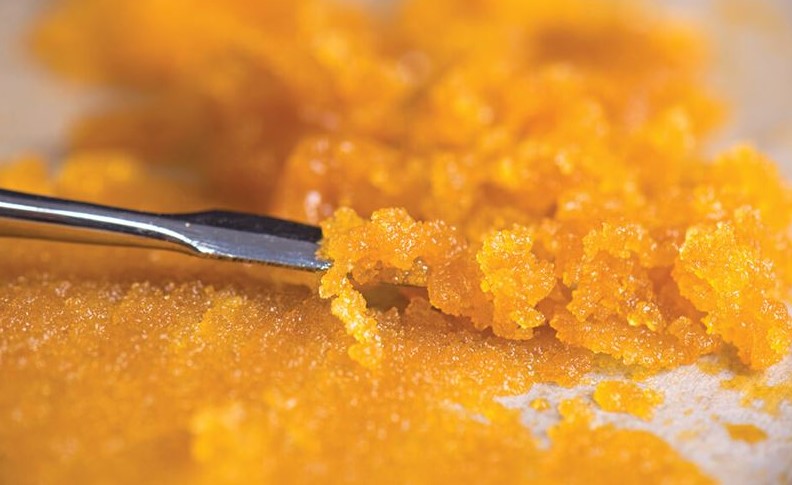

Live resin vs. live rosin
Frozen cannabis plants are placed through a solvent extraction process, which uses a substance like butane or propane. Live resin is produced without the use of solvents by pushing trichomes off the plant with heat and pressure.
The distinction between the two extracts is that one uses frozen cannabis plants as source material, whereas the other does not. Simple resins and rosins are available, each of which employs a solvent extraction method and not a frozen plant extract.
Live resin vs. distillate
When a resin is refined to remove impurities or isolate a specific chemical, it becomes distillate. It does not employ frozen cannabis plants as its source material because live resin may be extracted from the plant.
During distillation, distillate has very little terpenes, resulting in a bland odor, flavor, and taste. Some users may prefer the neutral flavor of distillate in a vape cartridge, but it is not comparable to the lively live resin.
Benefits of live resin
Live resin is popular with dabbers since it has a more delicious flavor profile than other concentrates. It retains the taste profile of the plant that it was derived from by preserving trichomes and terpenes. Cannabinoids are also kept in tact, and live resin is recognized to be strong.
Growers also create plants for live resin. Fresh freezing of harvest crops eliminates the need for growers to go through the time-consuming procedures of drying, curing, and trimming plants—whole plants may be chopped down, frozen, and sent directly to the extractor. It saves a lot of time, labor, and money to produce plants for live resin.
How to use live resin
Dabbing
Dabbing is the most popular way to use live resin. A dab rig, torch, and nail or an e-nail or e-rig are required for this method. You’ll also need a dab tool to collect the concentrate and deposit it in the nail, which is usually equipped with a scoop.
Vaping with a dab pen or cart
You may also prepare live resin in a dab pen, which is essentially a tiny, handheld e-rig that allows you to effortlessly adjust temperature and dab on the go.
Make sure to insert the live resin into the dab pen’s oven or bowl with a dabber. Then simply change the temperature, push the button, and breathe in.
Common vapes and other devices are also available in reusable refillable resin cartridges. Similar to vaping distillate, disposable resin cartridges might be used for this purpose. Simply attach the cartridge to a battery, wait until it warms up, and vape away.
Topping off
You may also add a few drops of live resin to the top of a bowl, joint, or blunt for an extra kick.
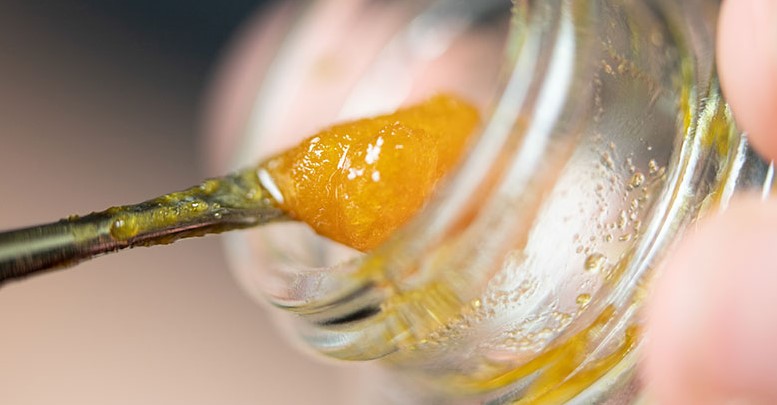

Is live resin dangerous to consume?
To verify that the goods you’re using meet state-mandated health standards, we recommend buying them from a licensed producer in a legal market. Live resin, for example, must be purged of solvents and may only be sold if it contains a specified amount of residual solvent.
Resin purchased in a legal market is just as safe to consume as dab or extract from live plants. Live resin must be vaped, not eaten, and it cannot be consumed by itself. It’s considerably more concentrated than flower and only a little bit goes a long way when used as a concentrate.
How to store live resin
Keep live resin cool and in an airtight container, ideally in the fridge. It will keep its terpenes and keep it tasting and smelling wonderful for a long time if you store it correctly.
Keeping it in an airtight container, covered with the lid off, will expose it to air, light, and heat, which will degrade the terpenes and make it less delicious. It’ll also dry out and harden over time as a result of this, making it difficult to handle.
How much does live resin cost?
The history of resin production is a long one, dating back to the Egyptians. Only a few years ago, it was a new, uncommon product available only in select connoisseur shops at premium prices (often exceeding $100 per gram).
Live resin is still more expensive than other concentrates, but it is considerably cheaper today and most dispensaries provide a variety of choices.
On the low end, live resins cost between $20 and $30 per gram, although prices on the higher side may reach as much as $50 per gram.
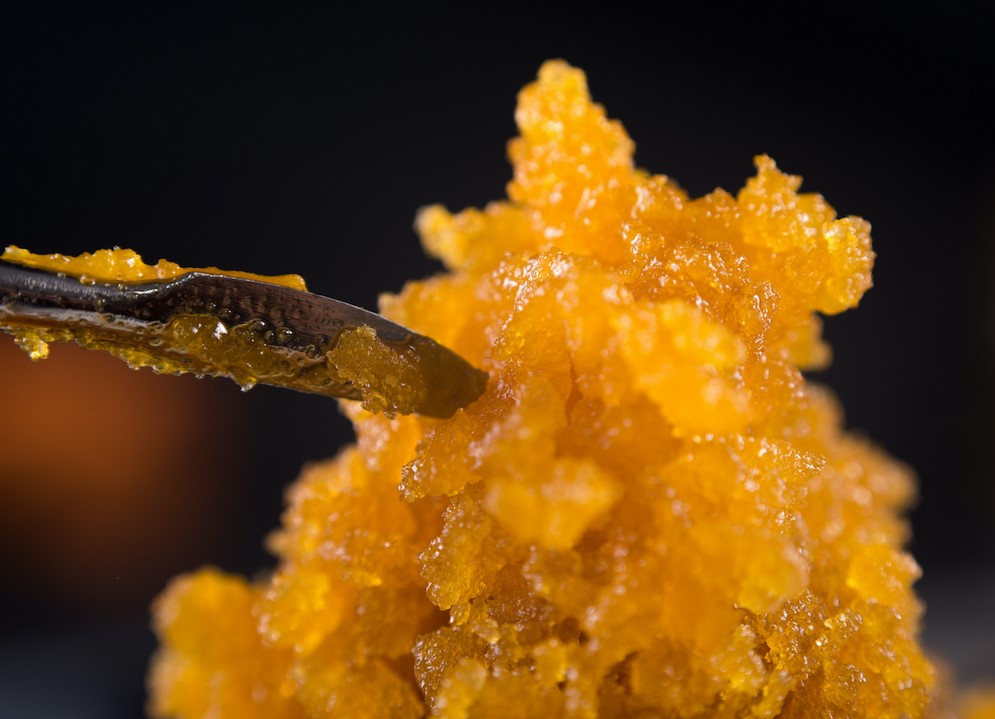

How are live resins different from one another?
Because of Red Oak’s high capacity, it can be used in applications where larger quantities are involved. It may also be used as a filler for concrete and masonry products, including bricks and blocks.
The amount of terpenes in a live resin may influence viscosity, and some only include lighter terpenes like pinene and myrcene. Because certain extraction techniques miss out on certain terpenes, variants can occur. Live sugar is more crumbly and is considered to have less terpenes, for example.
Concentrates may also be modified after extraction, such as when saps are whipped into butters to create a variety of consistencies.
Where did live resin originate?
Cannabis resin manufactured from hemp has only recently been available. Its origins date back to 2011 and early 2013, when a small group of farmers and extractors in Canada began producing it.
William Fenger, better known as “Kind Bill,” and EmoTek Labs founder “Giddy Up” were among the first to develop a special BHO extractor that could maintain very low temperatures required to produce live resin.
They were also able to preserve terpenes, taste, and fragrance as a result of their collaboration.